3. The characteristics of Web 1.0 and web 2.0
Dear friend,
A decade ago, participants working simultaneously on the same online document, or sharing it with dozens of people with just one click, would have been impossible. Today, these are simple everyday actions for almost all web users of personal, professional or educational needs. This unit offers an introduction to the development of web, from the beginning to present. Without this evolution no virtual mobility project would be possible.
At the end of the unit, you will be able to:
- Explain the difference between of Web 1.0 and Web 2.0;
- Identify the main features of Web 2.0;
- List and categorise the most important tools for Web 2.0.
This unit can be easily finished within 30 minutes.
1. Web 1.0 and Web 2.0
The terms: Web 1.0 and Web 2.0 are currently used to refer to two main stages in web development.
Web 1.0 refers to the period between 1990 and 2004.
Web 2.0 that was launched in 2004 refers to a new period, with a degree of higher development. As with all development, it refers to periods that overlap, the latter enriching the former.
Image 1: web development
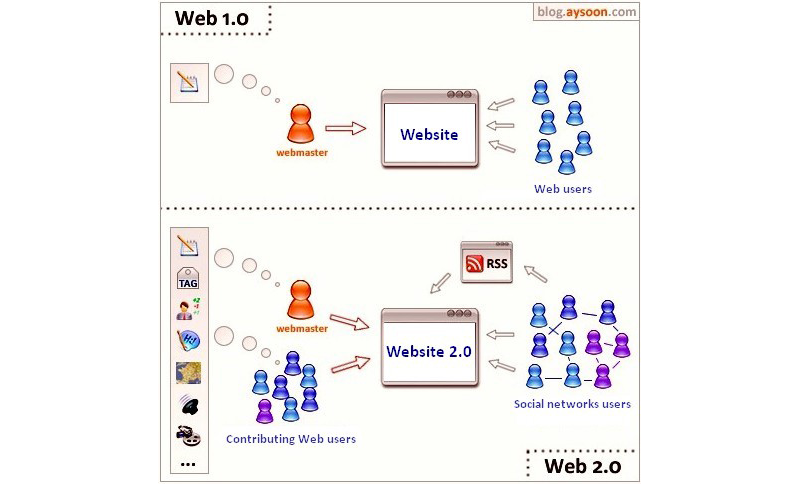
To discover the differences between terms of Web 1.0 and Web 2.0, we suggest that you look at this image, which illustrates both periods. Here are some explanations:
- The webmaster is responsible for a service, and the producer/author for the online content.
- RSS is an on-line resource where the content is produced automatically depending on the updates of another website (news for example).
- Social networks are sets of individual users, linked by social interactions. Facebook and Twitter are examples of on-line social networking portals.
Activity 1: Collaboration and dissemination
Look at again the previous image and answer the question:
Collaboration and dissemination. Both terms are used to characterise the features of Web 1.0 and Web 2.0. Which would you associate with Web 1.0 and Web 2.0?.
Activity 2: Dissemination
Web 1.0 is characterised by content transmission, dissemination. What similarities would you discover with other media?
Activity 3: Web 2.0 profile
How does the web user’s possibilities change with Web 2.0?
2. The main features of Web 1.0 and Web 2.0
The main features are summed up in the following table.
Development of a more participatory web |
|
Web 1.0 |
Web 2.0 |
Passive web user (reading) |
Active web user (content creation and sharing) |
Centralised information (controlled by the webmaster) |
Decentralised information (controlled by web users) |
Regularly central update of information |
Constantly changing information, regular updates by many individuals |
Static sites |
Dynamic sites |
Asynchronous communication |
Synchronous communication |
Hierarchical |
Networking |
Requires a lot of IT knowledge (for the webmaster) |
Requires little IT knowledge |
Purchased software |
Free online applications |
3. Tools for Web 2.0
Image 2 – Overview of Web 2.0 tool and services

Activity 4: Tools for Web 2.0
Look at the previous image, which shows a number of web 2.0 tools. How many do you recognise?
To help you discovering the world of web 2.0, we refer here to a classification that lets you regroup them using simple criteria. Each of the 4 categories will be explained in detail in the next units.
Classification of Web 2.0 tools: |
|
Capitalisation tools |
Disseminate, broadcast the content to a large number of users |
Cooperation tools |
Circulating the information Exchanging |
Collaboration tools |
Allows several people to work on the same artifact (document or application) |
Coordination tools |
Enabling project management and monitoring, to control and speed up interactions |
Activity 5: Matching exercise
In the following list, find two examples for each category of Web 2.0 tools (do not be discouraged if you are uncertain. You will have the chance to learn about them in the following units).
The portals, Skype software, wikis, emails, survey software, sites, planning software, Google Drive.
Classification of Web 2.0 tools: |
||
Capitalisation tools |
Disseminate the content to a large number of users |
|
1. |
2. |
|
Cooperation tools |
Circulating the information Exchanging |
|
1. |
2. |
|
Collaboration tools |
Allows several people to work on the same document or application |
|
1. |
2. |
|
Coordination tools |
Enabling project management and monitoring, to control and speed up interactions |
|
1. |
2. |
|
Congratulations!
You have finished the unit. We would like you to continue your training with the next unit, which will discuss capitalisation tools.

